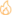IPO in India Risks: SEBI Compliance for Startups
By Filing Buddy . 16 Jan 26
On 30 April 2024, a small jewellery company, Varyaa Creations Ltd, raised ₹20.10 crore through an IPO on the BSE SME platform. But within hours of listing, over 71% of the funds, around ₹14 crore were siphoned off to unrelated entities, with one withdrawing ₹9 crore in just 16 minutes.
Shockingly, these transfers were labeled as IPO-related expenses, even though the prospectus listed only ₹60 lakh. This wasn’t a small error, it was a massive breach of trust and disclosure norms. SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) immediately froze the promoters’ shares, banned the company from raising further capital, and barred the lead manager from new IPO assignments.
Scary, right?
Here’s the truth: most startups don’t fail because of a bad product or weak idea. They fail due to small compliance mistakes, poor disclosures, and ignored regulations, mistakes that can cost millions and damage reputations overnight.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about going public in India, from eligibility and step-by-step process to the compliance rules you can’t ignore. By the end, you’ll know how to navigate the IPO maze confidently and avoid the pitfalls that tripped up startups like Varyaa Creations.
What Is an Initial Public Offering (IPO)?

An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is when a private company offers its shares to the public for the first time and gets listed on a stock exchange.
Think of it as opening your business to public investors, beyond friends, family, or private funds.
Going public isn’t just about raising money. It’s about accountability, transparency, and regulatory compliance. Once your company is listed, every move, profits, losses and governance is visible to the public, investors, and regulators.
Why Startups Opt for an IPO
Startups usually go public to:
- Raise capital for expansion, R&D, or operations
- Boost credibility with banks and partners
- Offer exits to early investors
- Attract better talent through stock options
But here’s the catch, an IPO is highly regulated, and skipping even one step can cost credibility, as Varyaa Creations learned the hard way.
Types of IPOs in India
In India, there are mainly two types of IPOs you should know about:
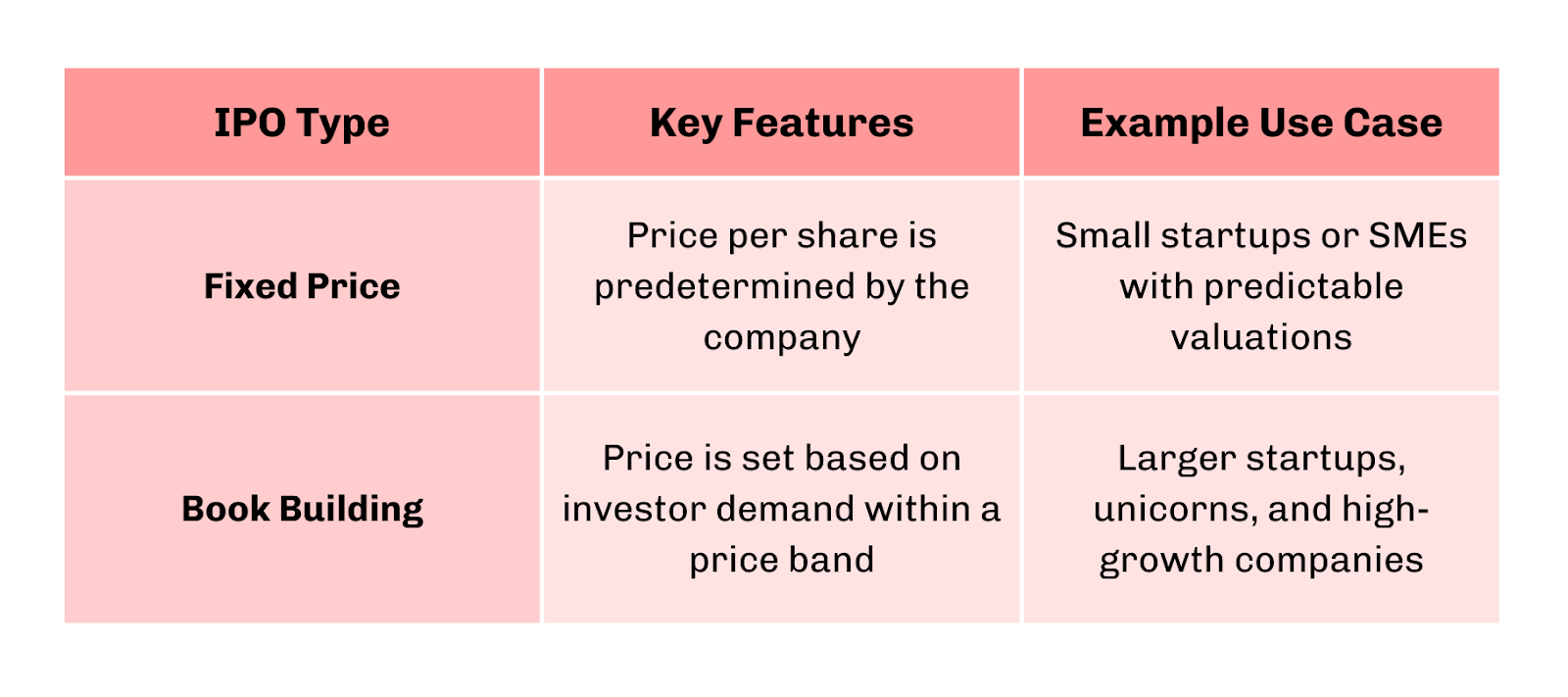
Choosing the right type matters. Fixed price is simple but less flexible, while book building allows the market to discover the best price, but comes with stricter compliance.
IPO Eligibility Criteria for Startups
Not every startup can just walk into an IPO. SEBI sets eligibility criteria to protect investors. Here’s a quick glance:
If your startup meets these benchmarks, you can begin the IPO journey.
But eligibility is only the starting point, staying compliant is the real challenge.
Next, let’s understand why compliance rules are non-negotiable.
SEBI Compliance for IPOs in India: Why It’s Non-Negotiable
So, you understand what an IPO is and how to get your startup listed.
Great! But here’s the reality: raising funds is just the start. The real test lies in following the regulatory framework that protects investors and ensures transparency.
Even tiny lapses in can lead to:
- Listing delays
- Heavy penalties
- Legal action against promoters
- Permanent damage to your startup’s credibility
Most IPO failures happen not because the business is weak, but because compliance is mishandled.
Key Regulations to Follow
Here’s what you need to focus on:
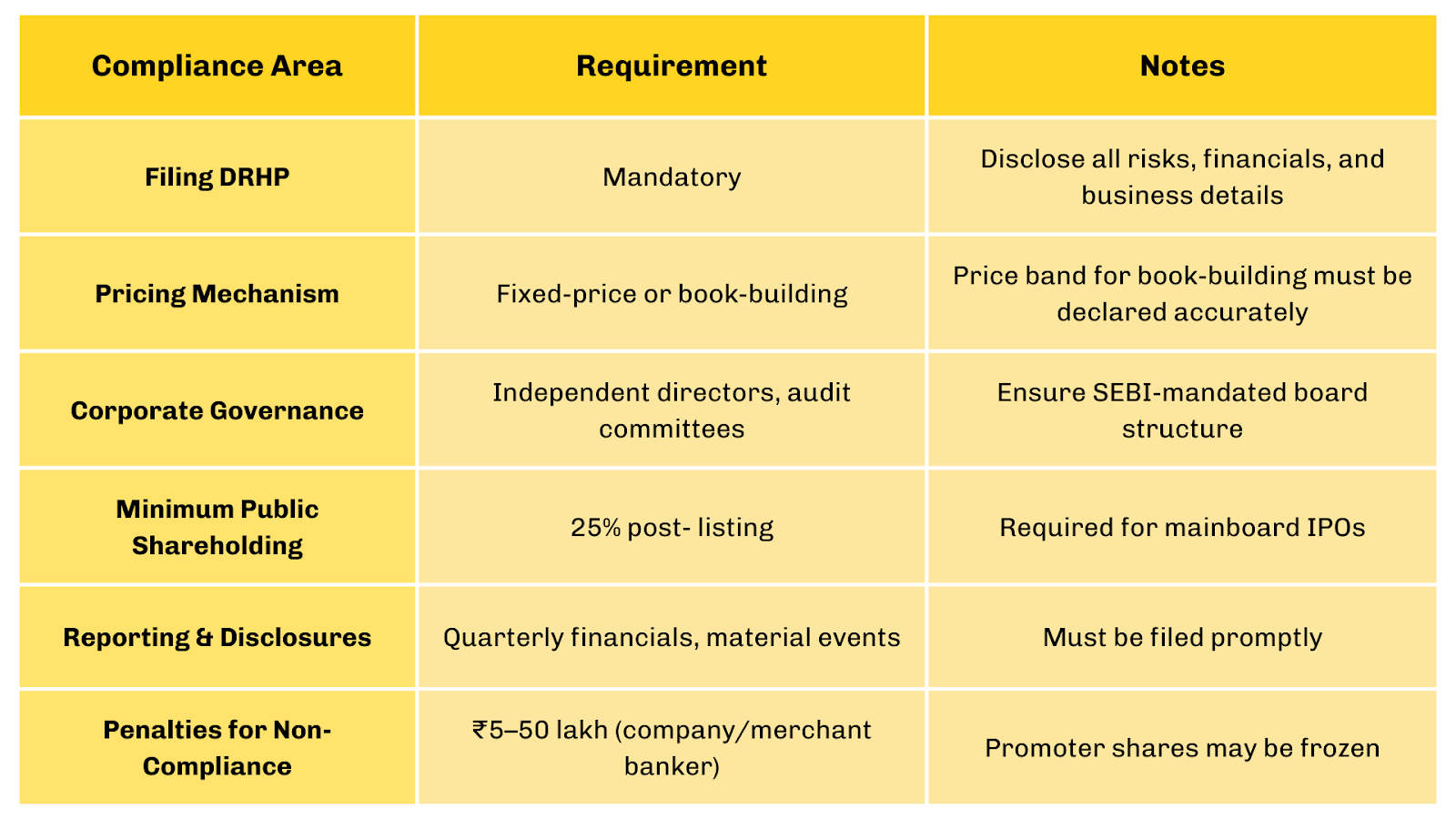
- Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP) filing: Must be submitted to SEBI for review.
- Full disclosure of financials and risks: Any misrepresentation can invite penalties or bar your IPO.
- Minimum public shareholding: SEBI mandates at least 25% of shares be held by public investors post-listing.
- Corporate governance norms: Board composition, audit committees, and independent directors must meet regulatory standards.
- Pricing compliance: Book-building or fixed-price mechanisms must follow guidelines.
Following these rules isn’t optional, it’s the backbone of your IPO’s credibility.
Common Compliance Requirements
Here’s a snapshot of critical compliance points every startup must meet:
Why Following SEBI Rules Is Crucial
Going public is exciting, but it comes with serious responsibilities. Rules exist to protect investors, ensure transparency, and maintain trust in the market. Even small lapses in disclosures, due diligence, or governance can lead to major consequences.
A clear example is the Gretex & Jayant Infratech IPO case.
SEBI found that Gretex, the merchant banker for Jayant Infratech’s listing, failed to properly verify and disclose how a large portion of the IPO funds would be used. Around 40% of the proceeds were meant for office space that was still under construction, but this wasn’t backed by proper documents or clearly communicated to investors.
It was also noted that Gretex did not meet the minimum net-worth requirement during an earlier financial year.
As a result, Gretex were barred from taking up new merchant banking assignments for 21 days, sending a strong message on the importance of due diligence and accurate disclosures.
This shows that non-compliance can result in:
- IPO delays or rejection
- Investor lawsuits
- Regulatory penalties
- Loss of credibility in the market
Even if your business is strong, one missed disclosure or weak verification process can derail the entire listing. And once investor trust is damaged, rebuilding it takes far more time and money than getting compliance right the first time.
Role of Merchant Bankers and Advisors
Most startups rely on merchant bankers or advisors to navigate compliance. Their responsibilities include:
- Reviewing DRHP and RHP documents
- Ensuring accurate disclosures
- Monitoring adherence to pricing and public shareholding norms
- Filing regulatory reports on time
Choosing the right advisors is critical, a small slip by them can cost your startup millions and your reputation.
In the next section, we’ll look at the IPO process in India and pinpoint where startups commonly fail, so you can prepare and stay compliant from day one.
IPO Process in India: Where Startups Often Fail
So, you’ve understood what an IPO is and why following rules are non-negotiable. Next comes the actual process of going public.
Let’s break it down step by step and see where founders often stumble.
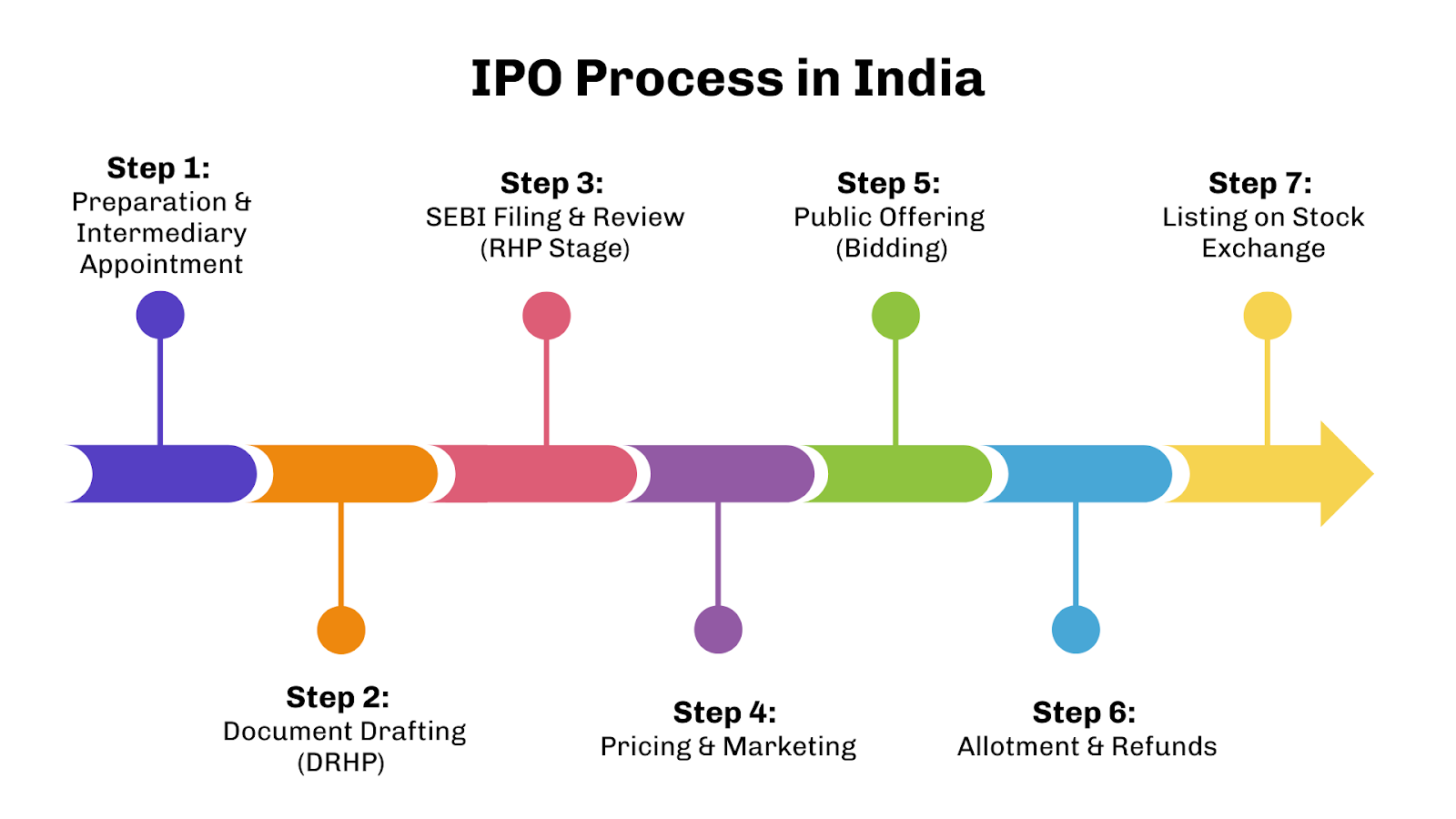
Step 1: Preparation & Intermediary Appointment
The journey begins with hiring merchant bankers, legal advisors, and auditors.
They conduct due diligence, assess eligibility, and prepare the company for SEBI scrutiny.
Common founder mistakes:
- Choosing inexperienced advisors
- Rushing eligibility checks
- Weak internal compliance systems
Step 2: Document Drafting (DRHP)
The Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP) is prepared with:
- Business and financial details
- Risk factors
- Fund utilisation plan
- Promoter and shareholding data
It clearly states that SEBI approval is pending.
Step 3: SEBI Filing & Review (RHP Stage)
The DRHP is submitted to SEBI.
SEBI issues observations and seeks clarifications.
After revisions, the Red Herring Prospectus (RHP) is filed with updated disclosures and the price band.
This is where many IPOs slow down due to:
- Delayed responses
- Weak explanations
- Incomplete disclosures
The National Stock Exchange (NSE) itself struggled with its long-planned IPO. Although it filed for listing in 2016, SEBI returned its documents in 2019 due to concerns around governance, equitable access for trading members, internal process gaps, and ownership issues. These compliance and governance problems led to multi-year delays in NSE’s public listing, proving that even major institutions can stumble if requirements aren’t met properly.
Step 4: Pricing & Marketing
For book-building IPOs:
- A price band (floor & cap) is set
- Roadshows are conducted
- Investor demand is tested
Overpricing or poor communication can hurt subscription levels.
Step 5: Public Offering (Bidding)
The IPO opens for 3–5 days.
Investors apply through ASBA via brokers or banks.
Mistakes here include:
- Poor investor guidance
- Technical issues
- Last-minute disclosure errors
Step 6: Allotment & Refunds
Shares are allotted (lottery system if oversubscribed).
Unsuccessful applicants receive refunds.
Delays here often lead to investor complaints.
Step 7: Listing on Stock Exchange
Shares are listed on NSE/BSE and public trading begins.
But compliance doesn’t end here.
Post-listing, companies must:
- File quarterly reports
- Disclose material event
- Maintain governance standards
The IPO process isn’t just a checklist, it’s a high-stakes journey where timing, accuracy, and compliance matter at every step. Most startups stumble not because the business is weak, but because they mismanage regulatory obligations or miss small compliance details.
And here’s the key point: even one overlooked rule or misreported figure can turn your IPO into a disaster, exactly what we’ll explore in the next section, where real startups like SBL Infratech faced serious consequences for compliance mistakes.
How Compliance Mistakes Can Destroy a Startup
By now, you’ve seen how the IPO process works and where startups commonly stumble. But understanding rules and processes isn’t enough, small compliance mistakes can have catastrophic consequences. Let’s look at a real-life example.
SBL Infratech: A Cautionary Tale
In 2025, SBL Infratech, along with its merchant banker Fast Track Finsec, faced the harsh reality of SEBI enforcement. Even though it was a smaller IPO, SEBI found false and misleading disclosures in the prospectus, including claims about project completions and utilization of funds that weren’t accurate.
The consequences were swift:
- SEBI imposed a ₹5 lakh penalty on SBL Infratech and ₹10 lakh on its merchant banker.
- The IPO’s credibility suffered, sending a warning to investors and the market.
- It highlighted how even minor IPOs are under strict scrutiny, and small lapses can have financial and reputational consequences.
This wasn’t about poor business fundamentals, the startup’s strategy could have been sound. It was regulatory oversights and weak verification that turned the IPO into a cautionary tale for founders everywhere.
Common Mistakes Startups Make
Most startups stumble in predictable ways. Knowing these in advance can save your IPO from disaster:

- Incomplete DRHP or RHP disclosures: Missing financials, risks, or shareholder info.
- Incorrect promoter or public shareholding reporting: Even minor errors can attract penalties.
- Delayed post-IPO filings: SEBI expects timely updates on financials and material events.
- Non-adherence to pricing or allotment rules: Mistakes can lead to investor complaints or refunds.
- Relying solely on internal teams: Without experienced advisors, compliance gaps are almost guaranteed.
A small oversight at any stage of the IPO process can quickly turn into serious regulatory trouble, just like it did for SBL Infratech. What starts as a “minor” compliance lapse can end up damaging your startup’s credibility, shaking investor confidence, and attracting unwanted scrutiny from SEBI.
The good news? These mistakes are avoidable.
In the next section, we’ll walk you through practical, founder-friendly tips to stay SEBI-compliant during your IPO, so you can move forward with clarity, confidence, and control.
Tips to Stay SEBI-Compliant During Your IPO
By now, you’ve seen what can go wrong. In most cases, it wasn’t the business idea that failed. It was compliance.
The good news? These mistakes are preventable. With the right preparation and guidance, you can navigate SEBI regulations smoothly and protect your IPO from unnecessary risks.
Here’s how to stay on the safe side:

1. Get Expert Guidance Early
Don’t treat compliance as a last-minute checklist. Involve experienced merchant bankers, legal advisors, and auditors from the very beginning. They help you:
- Review DRHP and RHP disclosures
- Meet filing timelines
- Align governance and pricing with regulations
Even strong internal teams can miss technical details. Structured support ensures nothing slips through the cracks.
2. Double-Check Every Disclosure
In an IPO, accuracy isn’t optional, it’s mandatory! Your prospectus must clearly reflect:
- How funds will be used
- Actual project status
- Real risks involved
- Correct promoter and shareholding details
Common mistakes include overstating progress, hiding risks, or misreporting ownership. A second review can save you from objections later.
3. Stick to Regulatory Timelines
SEBI follows strict schedules for:
- DRHP and RHP submissions
- Investor updates during book-building
- Post-IPO disclosures and financial reports
Even small delays can cause listing issues or regulatory action. Using structured compliance tracking systems, like Filing Buddy, helps startups stay organised and deadline-ready.
4. Be Transparent With Investors
Your credibility is your biggest asset during an IPO. Clear communication builds trust:
- Share real risks, not just growth stories
- Update investors on fund usage
- Avoid vague or exaggerated claims
Transparency reduces legal risks and strengthens investor confidence.
5. Audit Before You File
Before submitting anything:
- Recheck financial statements
- Verify promoter and public shareholding
- Confirm every claim in the prospectus
A clean internal audit makes your IPO documents stronger, clearer, and easier for SEBI to approve.
6. Learn From Past Mistakes
Cases like NSE’s IPO delays, Gretex’s due diligence lapses, and SBL Infratech’s disclosure issues show one thing clearly, small errors are not ignored.
Study these cases to understand:
- What SEBI flags most often
- How minor lapses become major penalties
- Why early compliance planning matters
An IPO rewards preparation and punishes shortcuts. The startups that succeed are the ones that treat compliance as a strategy, not a formality. When disclosures are accurate, timelines are respected, and advisors are involved early, the IPO process becomes far more predictable and far less stressful.
With the right systems, guidance, and attention to detail, your IPO doesn’t have to be a risk-filled gamble. It can be a confident step forward.
Final Thoughts: From IPO Fear to Founder Confidence
Going public is a big milestone, but only when it’s done right. The biggest lessons from real IPO failures are simple:
- Compliance comes first. Even small lapses can trigger serious consequences.
- Transparency builds trust. Investors back startups that disclose honestly.
- Preparation prevents panic. Early planning makes the public listing journey smoother.
The good news? With the right guidance and a compliance-first mindset, your IPO can be a growth story, not a warning tale.
If you want a simpler, stress-free way to stay on track, Filing Buddy is here to help you navigate SEBI requirements with confidence.
Because your IPO should build your future …not put it at risk.
FAQs
1. What is an IPO in simple words?
An IPO (Initial Public Offering) is when a private company sells its shares to the public for the first time and gets listed on a stock exchange like NSE or BSE.
2. Why do startups go for an IPO?
Startups raise funds, improve credibility, give exits to early investors, and attract better talent through public listing.
3. Who regulates IPOs in India?
SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) regulates all IPOs in India to ensure transparency and investor protection.
4. What is DRHP in an IPO?
The Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP) contains company details, financials, risks, and fund usage plans submitted to SEBI for approval.
5. What are SEBI compliance requirements for IPOs?
Startups must follow disclosure norms, governance rules, minimum public shareholding, pricing guidelines, and reporting timelines.
6. What happens if SEBI rules are not followed?
Non-compliance can lead to IPO delays, penalties, legal action, frozen promoter shares, and loss of investor trust.
7. Can SEBI stop an IPO?
Yes. SEBI can reject, delay, or return IPO filings if compliance issues or governance concerns are found.
8. What is the minimum eligibility for an IPO in India?
Startups need a minimum net worth, profit history (for mainboard), clean legal record, and public shareholding compliance.
9. What is the difference between SME IPO and Mainboard IPO?
SME IPOs are for smaller companies with simpler rules, while mainboard IPOs have stricter financial and compliance requirements.
10. Why was the NSE IPO delayed?
SEBI raised governance, ownership, and internal process concerns, causing multi-year delays in NSE’s IPO approval.
11. What mistakes do startups make during IPOs?
Common mistakes include incomplete disclosures, late filings, misreporting shareholding, weak due diligence, and poor governance.
12. What is the role of merchant bankers in an IPO?
They manage IPO filings, ensure compliance, coordinate with SEBI, and guide pricing, disclosures, and investor communication.
13. Can small IPOs also face SEBI penalties?
Yes. Even SME IPOs like SBL Infratech faced penalties for misleading disclosures.
14. How can startups avoid IPO compliance issues?
By hiring expert advisors, double-checking disclosures, meeting timelines, maintaining transparency, and using compliance tools.
15. Is SEBI compliance required after IPO?
Yes. Companies must continue reporting financials, material events, and governance updates even after listing.
Contact Us
An expert will call you within 24 hours. No payment required to get started.
Related Post

How to Obtain a Company Registration Number in India
Understanding Corporate Identification Numbers (CINs) and How to Obtain Them in India
. 2 mins.png)
Difference between Udyog Adhaar and Udyam Certificate
Want to get registered for Udyog Aadhar and Udyam Certificate? Here is their registration processes. Also, know about their differences. Explore their features, benefits, and processes to register online for each, helping you to choose the right option as per your need.
. 3 min read.png)
Changing Your Bank Signatory? Here are the Y Documents Required by Most Banks in India
Learn how bank signatory is important for financial workflow. Know why bank signatories are important and discover the documents required to change signature of your signatory.
. 5 min read